What is a “Wait” in Mahjong?
A wait (machi) in mahjong refers to the last tile(s) needed to complete a winning hand when you’re in tenpai, or the state of waiting itself. Tenpai means “one tile away from winning,” and which tile(s) you’re waiting for greatly affects your chances of winning and your strategy.
Understanding different types of waits is crucial for efficient hand building and reading your opponents’ waiting tiles.
Good Shape (Ryoukei) vs Bad Shape (Gukei)
Waits are broadly classified into “good shape (ryoukei)” and “bad shape (gukei).”
| Class | Acceptance | Characteristics | Representative Wait |
|---|---|---|---|
| Good Shape | 8 tiles | Easy to win, efficient | Ryanmen (Open Wait) |
| Bad Shape | 4 tiles or less | Hard to win, inefficient | Kanchan, Penchan, Tanki |
Building good shapes is fundamental to mahjong strategy. Even with the same tenpai state, good shapes have approximately twice the winning probability compared to bad shapes.
5 Basic Types of Waits
1. Ryanmen (Open Wait) [Good Shape]
The most efficient wait with 2 types of tiles
Characteristics
- Acceptance: 8 tiles (2 types × 4 tiles each)
- Efficiency: ★★★★★ (Best)
- Pinfu Requirement: Ryanmen wait is mandatory
Examples
| Hand Shape | Waiting Tiles |
|---|---|
  |   |
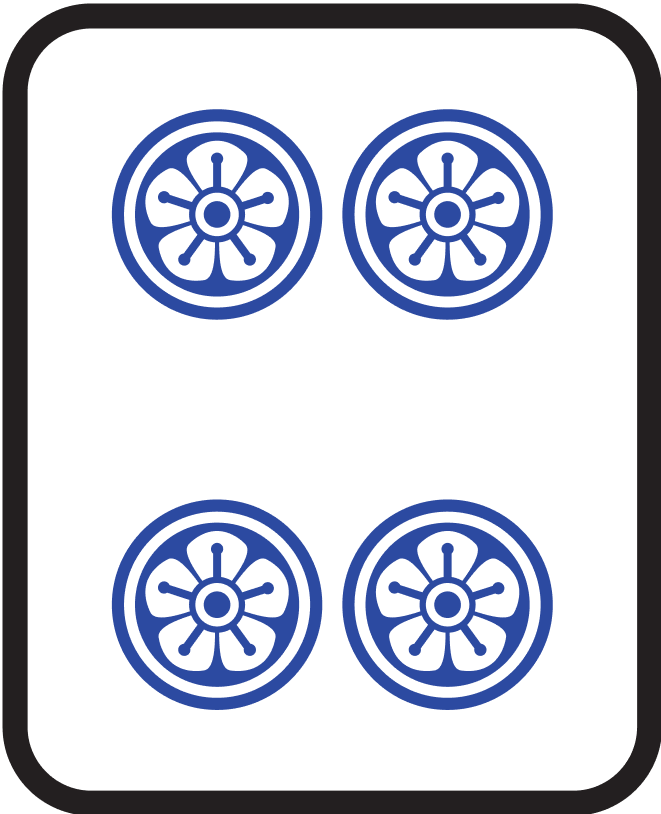  |   |
  |   |
Actual Formation
Completed hand:

Waiting for:
(8 tiles acceptance)
Key Points
- The most basic and powerful wait
- Formed with sequences 23-78 (12 or 89 don’t form ryanmen)
- Essential for pinfu yaku
For details: What is Ryanmen Wait?
2. Kanchan (Closed Wait) [Bad Shape]
Waiting for the middle tile of a sequence
Characteristics
- Acceptance: 4 tiles (1 type × 4 tiles)
- Efficiency: ★★☆☆☆
- Nickname: “Kan” or “Kanchan”
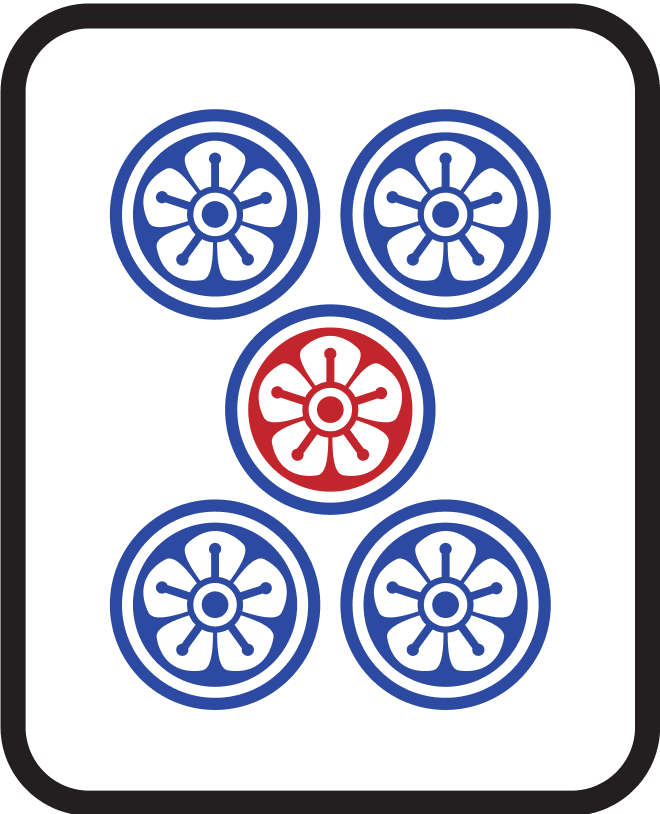
Examples
| Hand Shape | Waiting Tile | Description |
|---|---|---|
  |  | Waiting for 2 between 1 and 3 |
  |  | Waiting for 5 between 4 and 6 |
  |  | Waiting for 8 between 7 and 9 |
Actual Formation
Completed hand:



Waiting for:
(4 tiles acceptance)
Key Points
- Half as efficient as ryanmen wait
- Named after the tile being “stuck” (kan) between two others
- Try to convert to ryanmen whenever possible
For details: What is Kanchan Wait?
3. Penchan (Edge Wait) [Bad Shape]
Waiting for the edge tile with 12 or 89 shapes
Characteristics
- Acceptance: 4 tiles (1 type × 4 tiles)
- Efficiency: ★★☆☆☆
- Nickname: “Pen” or “Penchan”
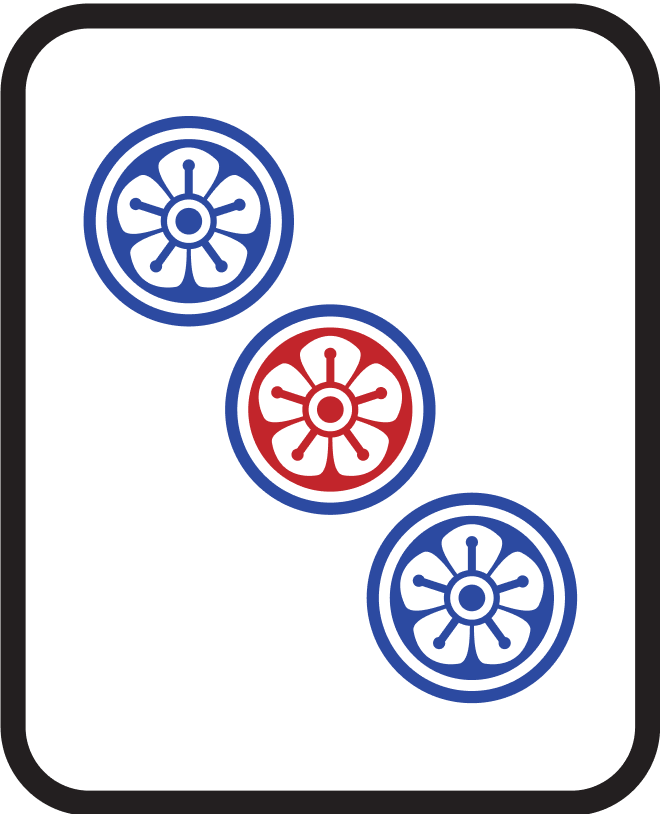
Examples
| Hand Shape | Waiting Tile | Description |
|---|---|---|
  |  | Waiting for 3 at the edge of 12 |
  |  | Waiting for 7 at the edge of 89 |
Actual Formation
Completed hand:



Waiting for:
(4 tiles acceptance)
Key Points
- Only 12→3 wait and 89→7 wait qualify
- 23→1 wait and 78→9 wait are ryanmen, not penchan
- Easy to make due to terminal tiles (1/9) but inefficient
For details: What is Penchan Wait?
4. Shanpon (Dual Pon Wait) [Bad Shape]
Waiting to complete either of two pairs into a triplet
Characteristics
- Acceptance: Usually 4 tiles (2 types × 2 tiles each)
- Efficiency: ★★☆☆☆
- Special Feature: Triplet-forming wait
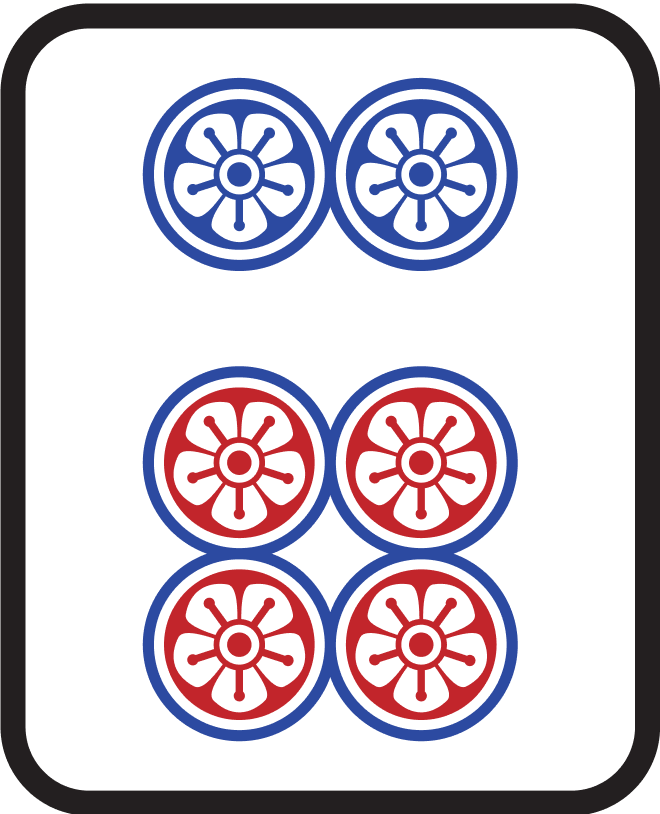
Examples
| Hand Shape | Waiting Tiles |
|---|---|
  and and   |   |
  and and   |   |
  and and   |   |
Actual Formation
Completed hand:



Waiting for:
(Usually 4 tiles acceptance)
Key Points
- Completes either pair into a triplet
- Actual acceptance varies based on visible tiles
- Good synergy with toitoi (all triplets) and honor tiles
For details: What is Shanpon Wait?
5. Tanki (Pair Wait) [Bad Shape]
Waiting for one tile to complete the pair (head)
Characteristics
- Acceptance: Maximum 3 tiles (1 type × 3 tiles)
- Efficiency: ★☆☆☆☆ (Lowest)
- Readability: ★★★★★ (Hardest to read)
Examples
| Hand Shape | Waiting Tile |
|---|---|
4 complete sets +  single single |  |
4 complete sets +  single single |  |
Actual Formation
Completed hand:



Waiting for:
(Maximum 3 tiles acceptance)
Key Points
- Lowest acceptance among all waits
- Advantage: very hard to read
- Chiitoi (seven pairs) is also a type of tanki wait
- Easy to change the waiting tile
For details: What is Tanki Wait?
Wait Types Comparison Table
Single Wait Comparison
| Wait Type | Shape Example | Waiting Tiles | Acceptance | Efficiency | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ryanmen (Open) |   |   | 8 tiles | ★★★★★ | Good |
| Kanchan (Closed) |   |  | 4 tiles | ★★☆☆☆ | Bad |
| Penchan (Edge) |   |  | 4 tiles | ★★☆☆☆ | Bad |
| Shanpon (Dual Pon) |     |   | 4 tiles | ★★☆☆☆ | Bad |
| Tanki (Pair) |  single single |  | 3 tiles | ★☆☆☆☆ | Bad |
Multi-Face Waits (Complex Waits)
Forms combining multiple waits are called multi-face waits (tamen machi). These increase acceptance and improve winning chances.
Two-Way Wait
Waiting for 2 types of tiles
Ryanmen + Ryanmen
Hand:Wait:
(Actually 3 types, but forms two ryanmen)
Ryanmen + Kanchan
Hand:Wait:
Three-Way Wait
Waiting for 3 types of tiles
Hand:Wait:
(Ryanmen + Kanchan + Ryanmen) Acceptance: 12 tiles
Nobetan (Extended Single Wait)
A special dual tanki wait from 4 consecutive tiles
Hand:Wait:
(2 types of tanki wait) Acceptance: 6 tiles (3 tiles + 3 tiles)
Looks like ryanmen but is actually a complex tanki wait.
Wait Selection and Hand Building Tips
1. Basic Principle: Aim for Good Shapes
The fundamental principle of mahjong hand building is always aiming for good shapes (ryanmen wait).
Bad Example (Prioritizing bad shape tenpai)




→ Discarding
for

shape,
kanchan wait (bad move)
Good Example (Keeping good shape potential)




→ Discarding
to maintain

shape (good move) → Drawing
creates
good shape potential
2. Shanten Count and Wait Relationship
| State | Description | Wait Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| 3+ Shanten | Still forming basic shape | Create many ryanmen proto-sequences |
| 2 Shanten | Creating set candidates | Be conscious of good shape transitions |
| 1 Shanten | One step before tenpai | Aim for good shape tenpai |
| Tenpai | One tile from winning | Wait shape is determined |
3. Wait Selection Based on Situation
Offensive Situations
- Prioritize ryanmen: Focus on speed
- Multi-face waits: Maximize acceptance
- Dora waits: Focus on points
Defensive Situations
- Tanki with safe tiles: Fold while keeping winning potential
- Waits using walls: Choose tiles likely to come out
- Avoid suji-dangerous waits: Avoid risky tiles
Techniques for Reading Waits
Reading Opponents’ Waits
Basic Suji Theory
If opponent discarded  , then
, then  and
and  are safe (suji) for ryanmen wait
are safe (suji) for ryanmen wait
| Discarded Tile | Safe Suji |
|---|---|
 |   |
 |   |
 |   |
 |   |
 |   |
 |   |
Reading from Shape
- Not discarding safe tiles early: Low probability of that tile wait
- Late-game honor tile discard: Possible tanki wait
- Keeping pairs: Possible shanpon or toitoi pursuit
Relationship Between Yaku and Waits
Pinfu
- Requirement: Must be ryanmen wait
- Cannot be completed with bad shapes
Chiitoi (Seven Pairs)
- Wait: Always tanki wait
- 6 pairs + tanki formation
Toitoi (All Triplets)
- Wait: Often shanpon or tanki wait
- Poor compatibility with ryanmen wait
Kokushi Musou (Thirteen Orphans)
- Wait: 13-way or tanki wait
- Special wait for special yaku
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Ryanmen or kanchan, which should I choose?
A. In most cases, choose ryanmen. With double the acceptance, winning probability differs significantly.
Q2. Is it okay to riichi with tanki wait?
A. Depends on the situation. While tanki has the advantage of being hard to read, if there’s potential for good shape transition, you should wait.
Q3. Bad shape tenpai or 1-shanten, which is better?
A. Generally, if there’s good shape potential, stay at 1-shanten. However, this changes based on point situation and remaining draws.
Q4. How to count multi-face waits?
A. Count the number of tile types you’re waiting for. Waiting for 

 is “three-way wait,” waiting for
is “three-way wait,” waiting for 
 is “two-way wait (ryanmen).“
is “two-way wait (ryanmen).“
3 Key Points for Beginners
1. Prioritize Ryanmen Wait
- Don’t rush tenpai; focus on building good shapes
- Good shape transition over bad shape tenpai
2. 12 and 89 are Penchan Waits

 →
→ wait is penchan (4 tiles)
wait is penchan (4 tiles)
 →
→
 wait is ryanmen (8 tiles)
wait is ryanmen (8 tiles)- Understanding this difference is crucial
3. Count Your Acceptance
- Good shape: 8 tiles
- Bad shape: 4 tiles or less
- This difference directly impacts win rate
Practice Problems
Problem 1: Basic Wait Identification
Hand:



Q. What wait? How many tiles acceptance?
See Answer
A. 
 ryanmen wait, 8 tiles acceptance
ryanmen wait, 8 tiles acceptance
Problem 2: Complex Wait
Hand:



Q. What wait? How many tiles acceptance?
See Answer
A. 

 three-way wait (Ryanmen + Kanchan + Ryanmen), 12 tiles acceptance
three-way wait (Ryanmen + Kanchan + Ryanmen), 12 tiles acceptance
Problem 3: Wait Selection
Hand:



Q. You drew  . What should you do?
. What should you do?
See Answer
A.
- Option 1: Discard
 for
for 


 shape,
shape, 
 ryanmen wait (recommended)
ryanmen wait (recommended) - Option 2: Discard
 for
for 


 shape,
shape,  kanchan wait (not recommended)
kanchan wait (not recommended)
Choose ryanmen wait.
Summary
Understanding wait types is one of the most important knowledge areas in mahjong hand building. Remember these key points:
- Good shapes (ryanmen) are fundamental: 8 tiles acceptance makes winning easier
- Avoid bad shapes: Acceptance is half or less
- Create multi-face waits: Increase acceptance with multiple waits
- Select waits based on situation: Balance offense and defense
- Read opponents’ waits: Infer from suji and hand shape
First focus on creating ryanmen waits, and as you improve, work on multi-face waits and situation-based wait selection. Understanding waits will definitely make you a stronger mahjong player!